
The hours the driver spends on service have been set to a certain limit by the transportation department. This includes the hours spent per day on service and the total hours spent throughout the week. These regulations have been established for the safety of drivers and to reduce the number of road accidents taking place due to the carelessness of drivers. The time restrictions ensure that the driver is well-rested after they are done with their service.
Dot Hours of Service
 The dot hours of service last 168 hours per week and limits how many hours can a truck driver drive each week. For example, if a driver starts at 12 p.m. in the afternoon on a Tuesday, he would have to continue his service till 12 p.m. of the next week’s Tuesday. The driving time of vehicle is restricted to 11 hours a day although the driver can be on service for 14 hours each day.
The dot hours of service last 168 hours per week and limits how many hours can a truck driver drive each week. For example, if a driver starts at 12 p.m. in the afternoon on a Tuesday, he would have to continue his service till 12 p.m. of the next week’s Tuesday. The driving time of vehicle is restricted to 11 hours a day although the driver can be on service for 14 hours each day.
According to hours of service rules, the service should begin after a 10-hour break between the services. After driving the vehicle for eight hours consecutively, the driver should take a mandatory break of at least half an hour. The hours of service should not include the breaks for filling fuel and meals. Over seven consecutive days, the driver can’t work over 60 hours on duty.
There is a rule known as 70/8 (70 hours in 8 days), also known as the dot 70-hour rule. The dot 70-hour rule limits the driver to driver no more than 70 hours in consecutive 8 days. The on-duty time together with the time spent on driving, should not be more than 70 hours.
Another regulation is the 14-hour rule. According to this rule, as soon as the driver begins his service and reports to be on duty, the 14 hours of his service begin. The 14-hour clock doesn’t stop even if the driver is not on duty or switches to sleeper berth mode during these 14 hours. According to dot regulations for truck drivers, once the 14 hours are completed, the driver is supposed to take a break of 10 hours before continuing with his service.
Split Sleeper Berth
The split sleeper berth was introduced to make the timings for truck drivers more flexible. It allows the drivers to divide their 10 hours break into shifts of two.
- The first shift should be taken between the 2nd and 8th hour. The driver can spend these hours on off-duty or on the sleeper berth.
- The second shift, however, should be spent in the sleeper berth.
- Both the shifts can be spent in any order as the driver wishes.
Log Book Rules
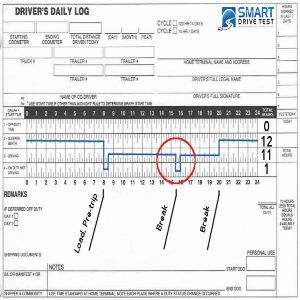 The logbook rules contain a certain set of instruction that the drivers must follow while they are on their service. Following are some of the rules the drivers should follow:
The logbook rules contain a certain set of instruction that the drivers must follow while they are on their service. Following are some of the rules the drivers should follow:
- The dot hours of service, mentioned above, should be regularly followed by the drivers.
- The drivers should always put safety first when driving commercial vehicles. The logbook rules keep the driver from being drowsy while he is driving by ensuring that he is well-rested.
- Hiding the hours of service can result in a penalty for the drivers. This includes any attempt to reset the ELD device in order to hide the hours of service. On the highway stops, the drivers might be inspected regarding their hours of service, and if any information is found to be missing, the driver would have to face legal consequences.
- The duty status needs to be constantly updated on whether the driver is on or off duty. The location and time need to be updated in every 24 hours.
ELD Exemptions
There are certain conditions in which the drivers can be exempted from using the ELD. Some of the electronic logs mandate exemptions are as follow:
- The driver has a commercial vehicle which was manufactured before the year 2000.
- The driver is conducting a towing away operation in which the unladen vehicles are transported.
Personal Conveyance Rules
The driver can use the commercial vehicle for personal conveyance only when he is on an off duty basic. At the time of using the vehicle for personal conveyance, the driver should be relieved from his duty. The vehicle can be used even when it is loaded as at the time the load is not being transported to its destination for benefitting the carrier. The vehicle can be used for different purposes like:
- The driver can use the vehicle for traveling to a nearby restaurant or entertainment spot.
- He can travel to a nearby safe location for having rest, and this can include his residence.
- The driver can use it to transport his personal property when not on duty.
FMCSA ELD
The ELD devices were introduced in order to easily record the time spent by drivers on duty and also to replace the obsolete method of recording data on paper. The ELD devices reduced the chance of any accidents as they restricted the number of hours the driver spent on duty. These devices were introduced to make the roads safer and free from hazards.
The ELDs have made the roads a safe space for commercial vehicle drivers. It has also made the process of recording data concerning hours spent on duty and off duty much easier and more accurate. The ELD works according to the rules set for hours of service and does not change any rules concerning the hours.
Among the ELD exemptions, is the 16-hour rule. According to this rule, the driver can be on duty for consecutive 16 hours, which means that he can work for an extra 2 hours. This exemption is applicable for drivers who start and end their service at the same location for five days consecutively. After the 16th hour, the driver has to be relieved from the duty.
Final Word
In order to promote road safety and to ensure one’s own safety, the commercial vehicle drivers should strictly follow the road safety rules which includes the use of ELD devices and following the regulations instructed in the log rule book. This helps in making the roads a safer space for everyone.




